近日,中南民族大学生命科学学院王海英研究小组实现了一种以Gluconacetobacter xylinus代谢产生细菌纤维素在线生物絮凝收集微藻的方法。该成果发表在Algal Research, Effective in situ harvest of microalgae with bacterial cellulose produced by Gluconacetobacter xylinus. (10.1016/j.algal.2018.09.002).并已申请相关专利。
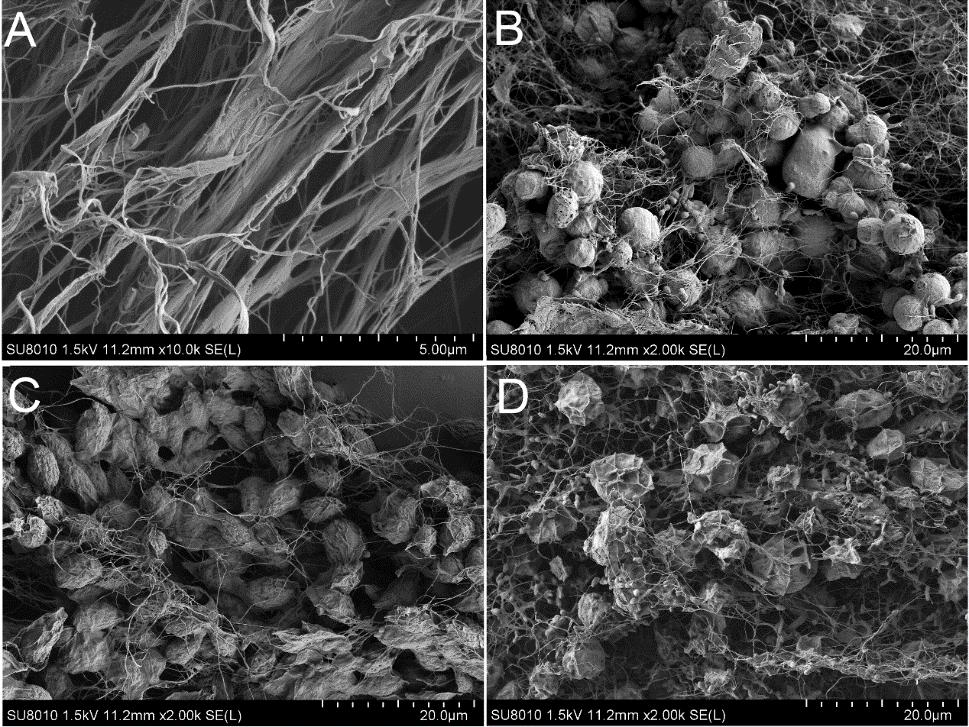
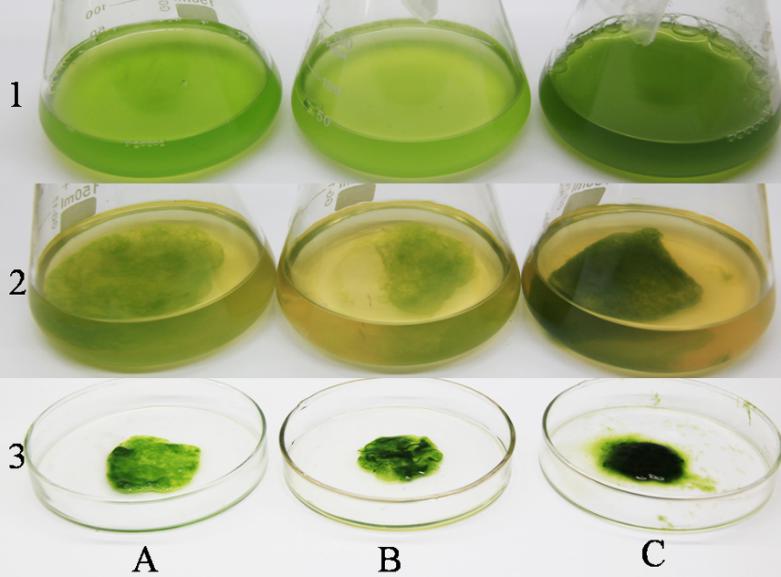
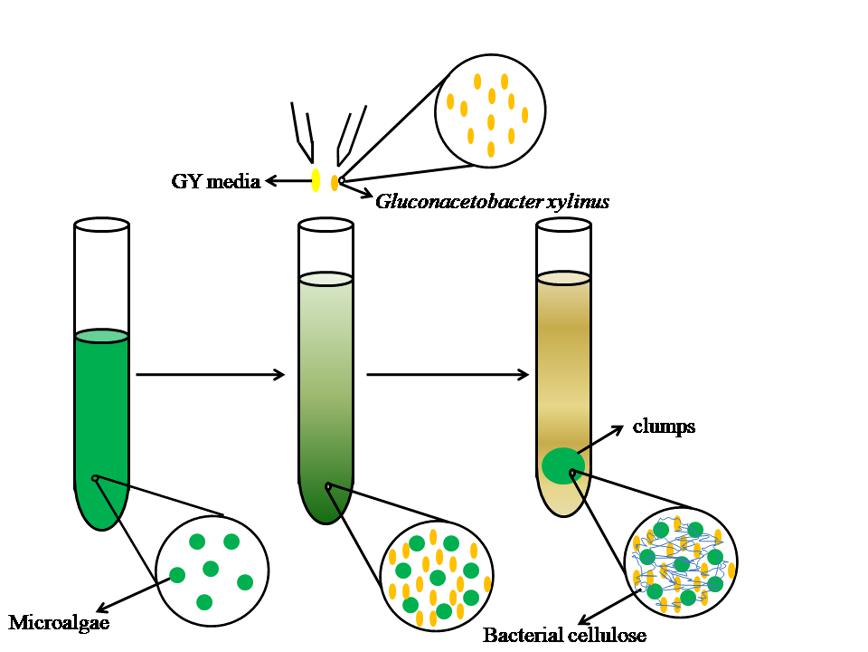
微藻采收技术成本高,需要发展更广泛、高效、低廉和环保的微藻采收方法。Gluconacetobacter xylinus产生的细菌纤维素具有很强的拉伸强度,低毒性和高亲水性的特点。本研究添加一定量的G.xylinus培养基至微藻培养液中,接种G.xylinus后代谢产生细菌纤维素可以有效地絮凝收集微藻,4hr内斜生栅藻和莱茵衣藻絮凝效率均达到了90 %以上,16hr内小球藻絮凝效率达到了90%以上,絮凝团块拉伸强度好,微藻不易泄露,易于收集。对微藻絮凝团块进行了电镜的观察,发现G. xylinus产生细菌纤维素成网状交联,将微藻细胞缠绕包裹在其中,从而达到絮凝的目的。
该方法容易操作,收集效率高,无毒且能保留微藻的活性,对微藻的后续加工和应用没有不良的影响,有望应用于微藻的食品工业、生物医药等领域的规模化生产。
Fig. 1. The harvesting process of microalgae cells by bacterial cellulose binding
Fig.2. Harvesting of C. vulgaris (A), S. obliqnus (B), and C. reinhardtii (C) from bacterial cellulose produced by G. xylinus. 1, algae alone; 2, algae embedded in bacterial cellulose; 3, the salvaged microalgal clumps.
Fig. 5. Scanning electron microscopy images of bacterial cellulose and clumps of microalgae in bacterial cellulose. Bacterial cellulose (A), C. vulgaris (B), S. obliqnus (C), and C. reinhardtii (D).