2018年1月18日,美国化学学会(ACS)有机化学领域权威期刊Organic Letters (影响因子6.6) 在线发表了浙江理工大学生命科学学院韩兵男教授团队与上海交大医学院林厚文教授团队在海洋蓝藻毒素Aplysiatoxins的活性靶标合作研究中取得的重要成果“Two Marine Cyanobacterial Aplysiatoxin Polyketides, Neo-debromoaplysiatoxin A and B, with K+ Channel Inhibition Activity”(DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03672)。

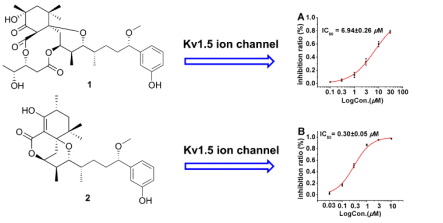
Aplysiatoxins一直以来被认为是一类有争议的海洋生物毒素,研究显示其具有PKC激酶激活作用,从而产生多种生物活性,促瘤、抗肿瘤及抗病毒等。本研究在采自中国南海的蓝藻Lyngbya sp.代谢物中首次发现了两个结构新颖的aplysiatoxins类似物,Neo-debromoaplysiatoxin A and B(化合物1-2)。 并运用现代波谱学手段,结合X-ray单晶衍射和ECD分子计算确定其平面及立体结构。研究人员使用钠离子通道(Nav1.5,Nav1.7,Nav1.8)和钾离子通道(hERG,Kv1.5,Kir2.1)对化合物1和2进行了活性筛选,结果显示化合物1和2只对钾离子通道Kv1.5有强烈抑制作用(IC50值分别为6.94±0.26 μM和0.30±0.05 μM)。
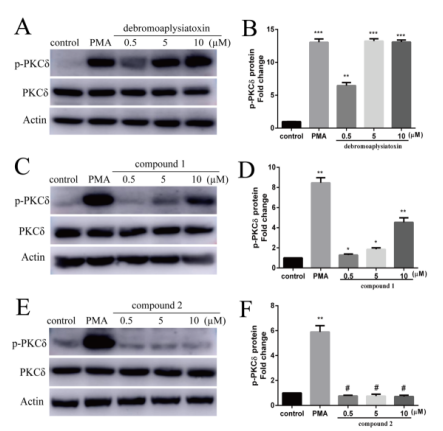
在PKC激酶激活实验中发现,化合物1和已知化合物debromoaplysiatoxin都能够促使PKC激酶磷酸化,而化合物2即使在10 μM的浓度下对PKCδ并没有显示任何激活作用。从结果推测,化合物2跟以往aplysiatoxins作为PKC激酶激活剂的调控机制不一样,是一种新型钾离子通道抑制剂,为今后研究aplysiatoxins作为PKC激酶激活剂来调控下游信号通路提供了不一样的思路。Kv1.5钾离子通道仅在人心房肌中表达,是一种房颤治疗的新靶点,特异性Kv1.5通道阻滞剂对心房具有高度选择性,不引发室性心律失常,极有可能成为未来心房颤动治疗的新型主导药物之一。